‡‡ Rod of Asclepius ‡‡
류마티스성 관절염 (Rheumatoid Arthritis) 본문
정의
지속적인 inflammatory synovitis (Peripheral Joint, symmetrical)
- Cartilage destruction & bone erosion 초래
- Joint deformity 유발
유전인자 - HLA-DR4와 관련
(그 외, SLE : HLA-DR 2,3 / Sjogren's syndrome : HLA-DR3 / Behcet's disease : HLA-B51 / multiple sclerosis : HLA-DR2 등... 더 자세한 것은 아래 테이블 참조 바람)
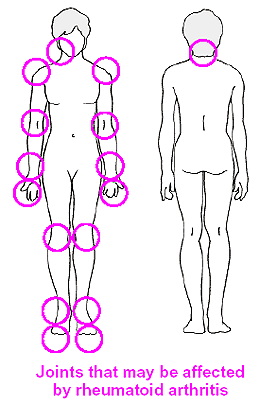
Symmetrical Arthritis
PIP, MCP joint involvement - DIP joint는 드물다. (Osteoarthritis에서 흔함)
Axial involvement - Upper cervical spine에 한정됨, Lumbar spine 침범은 드묾.
관절 외 증상
-Rheumatic nodule (20~30%) : Circulating RF(+) 환자에서 주로 나타남
-Weakness & atrophy of skelectal m.
-Rheumatoid vasculitis
-Pleuropulmonary manifestation : pleural disease, interstitial fibrosis, pulmonary nodule, pneumonitis
-pericarditis : 흔하지만 대개 무증상
-nerve entrapment : atlantoaxial or midcervical spine subluxation에 의해
-eye : episcleritis, scleritis, Uevitis
-felty's syndrome : chronic RA + splenomegaly + neutropenia
-osteoporosis
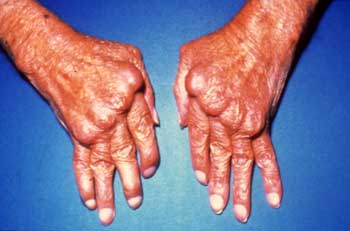
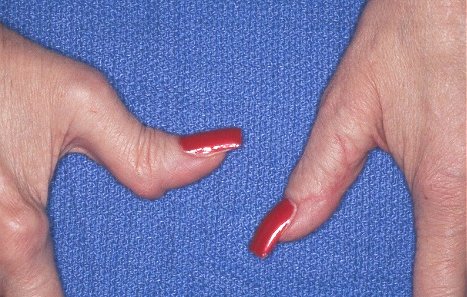
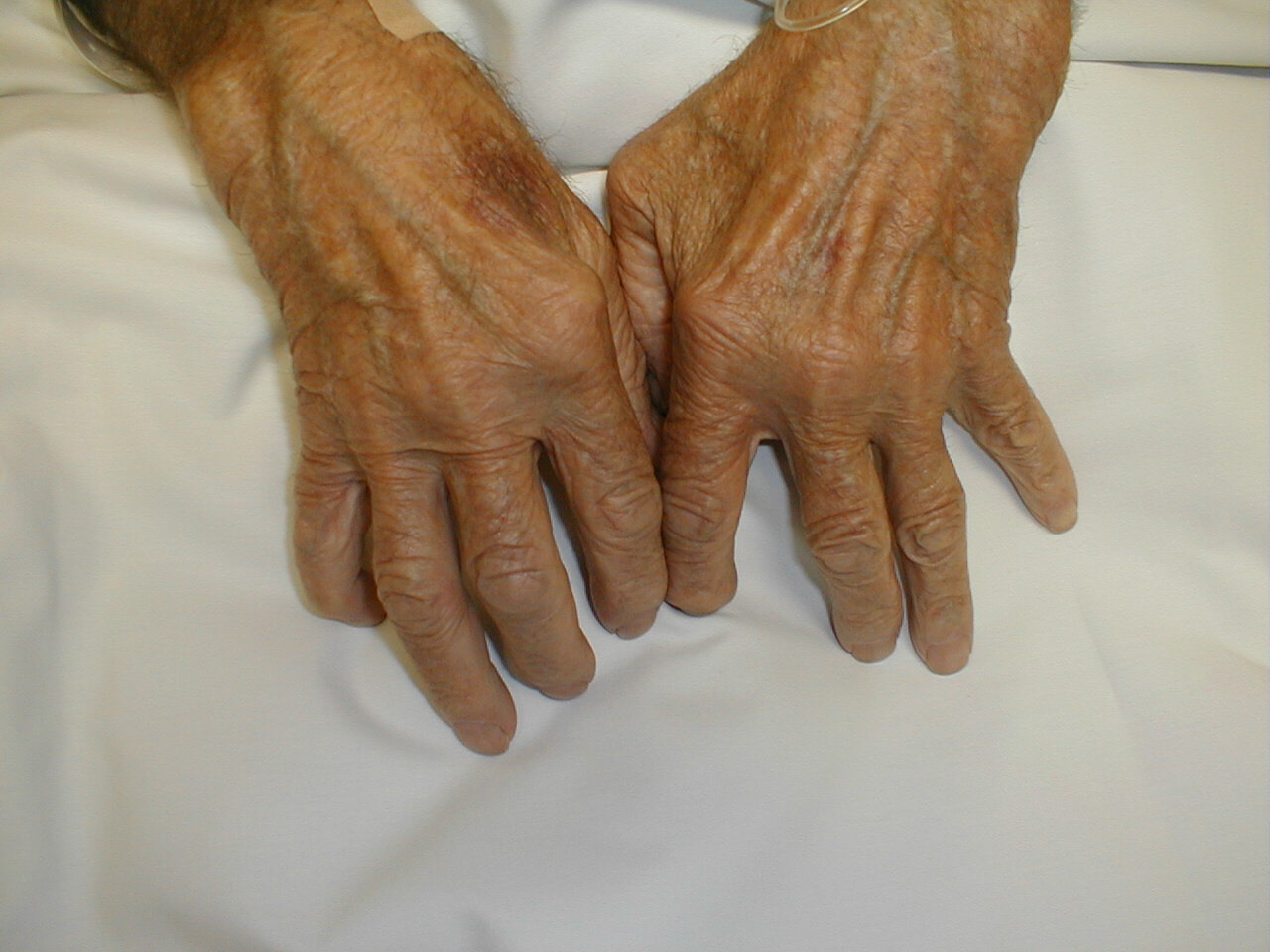
손
- Z deformity
- Swan-neck deformity
- Boutonniere deformity
- Hyperextension of the first interphalangeal joint & flexion of the first metacarpophalangeal joint with a consequent loss of thumb mobility & pinch
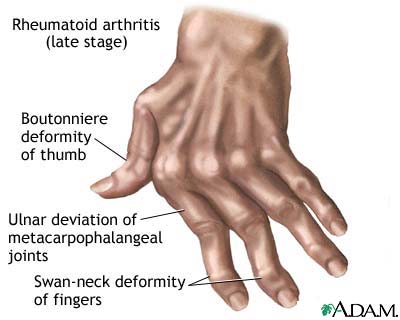
진단

Lab Finding
Rheumatic Factor
- 종류로 IgM, IgG, IgA가 있으며 IgM이 가장 흔하다.
- 건강한 사람에서도 5% 정도 발견되며, 나이가 증가함에 따라 더 많아져 65세 이상에서는 10~20%가 (+)
- 다른 RF(+) 질환
SLE, Sjogren's syndrome, chronic liver disease, sarcoidosis, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
Infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis B, tuberculosis, leprosy, syphilis
subacute bacterial endocarditis,visceral leishmaniasis, schistosomiasis, malaria
- 정상인에서도 수혈이나 백신 접종 후 나타난다.
- 진단적 의미는 없으나 존재할 경우 예후가 좋지 않음을 의미한다.
- Screening으로는 유용하지 않지만 의심되는 임상 증상이 있을 때 확진 수단으로 사용될 수 있다.
관절액의 양상
- Turbid, yellow, viscosity ↓, protein ↑
- WBC 2000~50000 (PMN>70%)
- glucose concentration - normal or slightly ↓ (혈청 포도당 농도의 1/2정도)
- 보체 감소 (serum의 보체치는 낮지 않음, 그리고 gout와 osteoarthritis는 정상임)
- 비교 : Osteoartiritis [ Yellow, transparent, WBC < 2000, PMN < 25% ]
Trauma [ Red, Opaque, WBC < 3000, PMN < 25% ]
치료
목표
- 통증의 완화
- 염증의 감소
- 관절 구조의 보호
- 기능의 유지
- 전신적 증상의 조절
약물
- Aspirin, NSAID, simple analgesics, 필요 시 low dose glucocorticoid : 주로 pain control
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs(DMARDS)
NSAID와 병용하여 사용한다. ESR, CRP, RF 감소, 증상 호전 효과 보인다.
* Gold compound
* D-penicillamine
* Antimalarial drug - Chloroquine, hydrochloroquine - 가장 많이 쓴다.
* sulfaslalzine
* MTX
- Glucocordicoid
- Immunosuppressive Tx : Azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporin
- TNF-α agent : Etanercept, Infliximab 등
- Cytotoxic Agent
예후
나쁜 예후인자로 다음과 같은 것들이 있다.
Classic pattern, 1년 이상 지속될 때, 고령에서 발병, 관절 외 증상 존재시, insidious onset
radiologic joint erosion, 혈청 RF 높을 때, Rheumatic nodule 존재 시, 여성
Raynaud Phemonon (+), HLA-DR4, CRP & ESR ↑, haptoglobin
20개 이상의 joint involve시, functional disability 존재 시, 다른 질환 동반했을 때
low socioeconomic status or educational level
※ Disease Activity 반영하는 것
- Morning stiffness의 length & intensity
- Anemia, Thrombocytosis
- ESR, CRP
※ 참고 사이트
류마티스 환자의 진단에 대하여
http://www.arthritis.co.za/the%20clinical%20examination%20technique.html
증례보고 - 류마티스성 관절염
http://uwmsk.org/residentprojects/rheumatoid.html
지속적인 inflammatory synovitis (Peripheral Joint, symmetrical)
- Cartilage destruction & bone erosion 초래
- Joint deformity 유발
유전인자 - HLA-DR4와 관련
(그 외, SLE : HLA-DR 2,3 / Sjogren's syndrome : HLA-DR3 / Behcet's disease : HLA-B51 / multiple sclerosis : HLA-DR2 등... 더 자세한 것은 아래 테이블 참조 바람)
임상 증상
Pain : 움직일 때 심해짐.
Generalized Stiffness : 1시간 이상 지속되는 Morning Stiffness

Symmetrical Arthritis
PIP, MCP joint involvement - DIP joint는 드물다. (Osteoarthritis에서 흔함)
Axial involvement - Upper cervical spine에 한정됨, Lumbar spine 침범은 드묾.
관절 외 증상
-Rheumatic nodule (20~30%) : Circulating RF(+) 환자에서 주로 나타남
-Weakness & atrophy of skelectal m.
-Rheumatoid vasculitis
-Pleuropulmonary manifestation : pleural disease, interstitial fibrosis, pulmonary nodule, pneumonitis
-pericarditis : 흔하지만 대개 무증상
-nerve entrapment : atlantoaxial or midcervical spine subluxation에 의해
-eye : episcleritis, scleritis, Uevitis
-felty's syndrome : chronic RA + splenomegaly + neutropenia
-osteoporosis



손
- Z deformity
- Swan-neck deformity
- Boutonniere deformity
- Hyperextension of the first interphalangeal joint & flexion of the first metacarpophalangeal joint with a consequent loss of thumb mobility & pinch

진단

Lab Finding
Rheumatic Factor
- 종류로 IgM, IgG, IgA가 있으며 IgM이 가장 흔하다.
- 건강한 사람에서도 5% 정도 발견되며, 나이가 증가함에 따라 더 많아져 65세 이상에서는 10~20%가 (+)
- 다른 RF(+) 질환
SLE, Sjogren's syndrome, chronic liver disease, sarcoidosis, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
Infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis B, tuberculosis, leprosy, syphilis
subacute bacterial endocarditis,visceral leishmaniasis, schistosomiasis, malaria
- 정상인에서도 수혈이나 백신 접종 후 나타난다.
- 진단적 의미는 없으나 존재할 경우 예후가 좋지 않음을 의미한다.
- Screening으로는 유용하지 않지만 의심되는 임상 증상이 있을 때 확진 수단으로 사용될 수 있다.
관절액의 양상
- Turbid, yellow, viscosity ↓, protein ↑
- WBC 2000~50000 (PMN>70%)
- glucose concentration - normal or slightly ↓ (혈청 포도당 농도의 1/2정도)
- 보체 감소 (serum의 보체치는 낮지 않음, 그리고 gout와 osteoarthritis는 정상임)
- 비교 : Osteoartiritis [ Yellow, transparent, WBC < 2000, PMN < 25% ]
Trauma [ Red, Opaque, WBC < 3000, PMN < 25% ]
치료
목표
- 통증의 완화
- 염증의 감소
- 관절 구조의 보호
- 기능의 유지
- 전신적 증상의 조절
약물
- Aspirin, NSAID, simple analgesics, 필요 시 low dose glucocorticoid : 주로 pain control
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs(DMARDS)
NSAID와 병용하여 사용한다. ESR, CRP, RF 감소, 증상 호전 효과 보인다.
* Gold compound
* D-penicillamine
* Antimalarial drug - Chloroquine, hydrochloroquine - 가장 많이 쓴다.
* sulfaslalzine
* MTX
- Glucocordicoid
- Immunosuppressive Tx : Azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporin
- TNF-α agent : Etanercept, Infliximab 등
- Cytotoxic Agent
예후
나쁜 예후인자로 다음과 같은 것들이 있다.
Classic pattern, 1년 이상 지속될 때, 고령에서 발병, 관절 외 증상 존재시, insidious onset
radiologic joint erosion, 혈청 RF 높을 때, Rheumatic nodule 존재 시, 여성
Raynaud Phemonon (+), HLA-DR4, CRP & ESR ↑, haptoglobin
20개 이상의 joint involve시, functional disability 존재 시, 다른 질환 동반했을 때
low socioeconomic status or educational level
※ Disease Activity 반영하는 것
- Morning stiffness의 length & intensity
- Anemia, Thrombocytosis
- ESR, CRP
※ 참고 사이트
류마티스 환자의 진단에 대하여
http://www.arthritis.co.za/the%20clinical%20examination%20technique.html
증례보고 - 류마티스성 관절염
http://uwmsk.org/residentprojects/rheumatoid.html